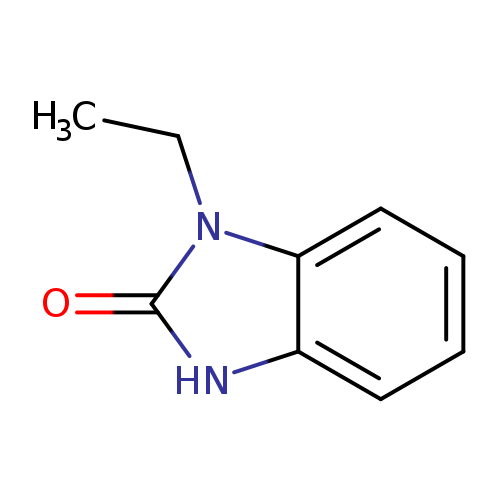
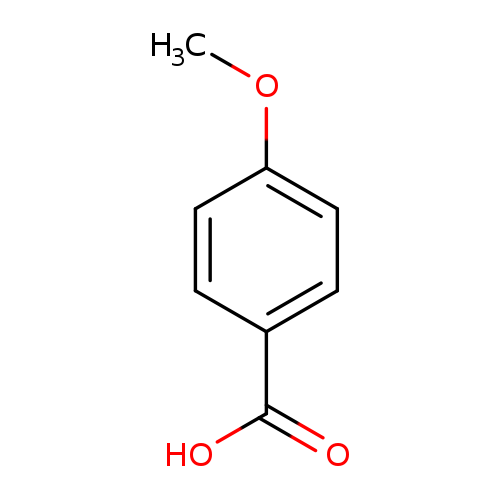
-
PRODUCTS
- Pharmaceutical Intermediates
- Antispasticity Agents
- Anesthetics
- Anti-Addiction Agents
- CNS Agents
- Genetic/Enzyme Disorder
- Analgesics
- Anti-inflammatory Agents
- Dermatological Agents
- Anxiolytics
- Antiparkinson Agents
- Antipsychotics
- Antidementia Agents
- Antiparasitics
- Genitourinary Agents
- Antigout Agents
- Electrolytes
- Sleep Disorder Agents
- Antidepressants
- Gastrointestinal Agents
- Antibacterials
- Blood Products
- Anticonvulsants
- Blood Glucose Regulators
-
Cardiovascular Agents
- Clevidipine Butyrate
- Choline Fenofibrate
- Binodenoson
- Bempedoic acid
- Avanafil
- Arbutamine
- Allisartan Isoproxil
- Vardenafil
- Udenafil
- Satavaptan
- Tecadenoson
- Silodosin
- Sacubitril
- Pratosartan
- Oxodipine
- Otenzepad
- Palonidipine
- Omapatrilat
- Moexipril
- Lixivaptan
- Lemildipine
- Landiolol
- Finerenone
- Dofetilide
- Darodipine
- Respiratory Tract
- Antivirals
-
Antineoplastics
- Cositecan
- Canfosfamide
- Cabozantinib
- Buparlisib
- Bropirimine
- Bosutinib
- Binimetinib
- BAL-101553
- AT-7519
- ASLAN-002
- Arzoxifene
- Apaziquone
- Apalutamide
- Anastrozole
- Amifostine
- Aldoxorubicin
- Afatinib
- Acadesine
- ZSTK-474
- Zoptarelin Doxorubicin
- Zibotentan
- Vosaroxin
- Volitinib
- Venetoclax
- Vadimezan
- Upamostat
- Tyroserleutide
- Tirabrutinib
- Tazemetostat
- Taselisib
- Talazoparib
- Taladegib
- Talabostat
- Talaporfin
- Sorafenib
- Tacedinaline
- Sonidegib
- Semaxanib
- Selinexor
- Sapacitabine
- Seliciclib
- Rociletinib
- Riviciclib
- Rimiducid
- Ribociclib
- Ralimetinib
- Quizartinib
- Prinomastat
- Pimasertib
- Phenoxodiol
- PD-0325901
- Orantinib
- Ombrabulin
- Nolatrexed
- Niraparib
- Nintedanib
- MK-2206
- Methyl Aminolevulinate
- Midostaurin
- Iniparib
- Infigratinib
- Ilorasertib
- Idelalisib
- Idasanutlin
- Galunisertib
- Glufosfamide
- Galeterone
- Firtecan pegol
- Forodesine
- Fedratinib
- Evofosfamide
- Enobosarm
- Endoxifen
- Emivirine
- Dexanabinol
- Disomotide
- Dactolisib
- Darinaparsin
- Dabrafenib
- Immunological Agents
- Antifungals
- Metabolic Bone Disease
- Ophthalmic Agents
- Inhibitors/Agonists
- Protease
-
Metabolic Enzyme
- COMT
- CETP
- Cathepsin
- Carbonic Anhydrase
- ATP Citrate Lyase
- Aminopeptidase
- Aldose Reductase
- ALDH
- Adenosine Receptor
- Adenosine Kinase
- AhR
- Adenosine Deaminase
- ACE
- ACC
- 5 Alpha Reductase
- 15-PGDH
- Xanthine Oxidase
- VD/VDR
- Transferase
- Thrombin
- Thioredoxin
- SPHK
- SGK
- SCD
- ROR
- Renin
- RAR/RXR
- Phosphorylase
- Phospholipase
- PDHK
- PDE
- P450
- Mineralocorticoid Receptor
- NAMPT
- MAO
- LXR
- Lipoxygenase
- Lipase
- IDO
- IDH
- Hydroxylase
- HMGCR
- HIF
- Hexokinase
- GST
- GLUT1
- Glucokinase
- FXR
- Ferroptosis
- FAS
- Factor Xa
- FAAH
- Elastase
- DGAT
- DHFR
- Dehydrogenase
- Decarboxylase
- CPA
- MAPK/ERK Pathway
- JAK/STAT Signaling
-
GPCR/G Protein
- Cholecystokinin Receptor
- CaSR
- Cannabinoid Receptor
- cAMP
- Bradykinin Receptor
- Angiotensin Receptor
- Adenosine Receptor
- Vasopressin Receptor
- TSH Receptor
- RGS
- Ras
- PAR
- PAFR
- Prostaglandin Receptor
- P2Y Receptor
- OXTR
- OX Receptor
- Opioid Receptor
- NMUR
- Neurotensin Receptor
- Neuropeptide Y receptor
- Motilin Receptor
- LPL Receptor
- LPA Receptor
- Guanylate Cyclase
- GNRH Receptor
- Glucagon Receptor
- GHSR
- Endothelin Receptor
- Epigenetics
- Endocrinology/Hormones
- DNA Damage
- Cytoskeleton
- Cell Cycle
- Biochemical Reagents
- Immunology/Inflammation
- Autophagy
- Apoptosis
- Anti-infection
- Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase/RTK
- Ubiquitin
- Stem Cells/Wnt
- Biochemical Reagent
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Other Inhibitors
- Natural Products
- ADCs
- Chemistry
- Chemical Biology
- Stains and Dyes
- Specialty Synthesis
- Synthetic Reagents
- Asymmetric Synthesis
-
Catalysis Chemistry
- Diketone Ligands
- Cross-Coupling using Transition Metal Catalysts
- Cross-Coupling
- Carbon-Donor Ligands
- C-H Activation
- Transition Elements
- Photocatalysts
- Rare-Earth Elements
- Phosphorous Compounds
- Organocatalysts
- Olefin Metathesis
- Olefin Ligands
- Non-Precious Metal Catalysts
- Nitrogen-Donor Ligands
- Main-Group Elements
- Hydrogenation
- Metal Catalysts
-
Heterocyclic Building Blocks
- Furans
- Epoxides
- Dioxoles
- Dioxolanes
- Cinnolines
- Carbazoles
- Benzoxazoles
- Benzothiophenes
- Benzothiazoles
- Benzofurans
- Benzodioxans
- Benzisoxazoles
- Benzimidazoles
- Azetidines
- Acridines
- Triazoles
- Triazines
- Thiomorpholines
- Thiophenes
- Thiazolidines
- Thiazoles
- Thiazines
- Thiadiazoles
- Tetrazoles
- Tetrahydroquinolines
- Tetrahydropyrans
- Tetrahydroisoquinolines
- Tetrahydrofurans
- Spiroes
- Quinuclidines
- Quinoxalines
- Quinolines
- Quinazolines
- Pyrrolines
- Pyrroles
- Pyrrolidines
- Pyrimidines
- Pyridazines
- Pyridines
- Pyrazoles
- Pyrans
- Pyrazines
- Purines
- Piperidines
- Piperazines
- Phthalazines
- Oxetanes
- Oxazolines
- Oxazolidines
- Oxazoles
- Oxazines
- Oxadiazoles
- Other Aromatic Heterocycles
- Naphthyridines
- Other Aliphatic Heterocycles
- Isothiazoles
- Isoxazoles
- Morpholines
- Isoquinolines
- Indolines
- Indoles
- Imidazolines
- Indazoles
- Imidazolidines
- Imidazoles
-
Organic Building Blocks
- Aryls
- Anhydrides
- Amines
- Amidines
- Amides
- Alkynyls
- Alkyls
- Alkenyls
- Aliphatic Cyclic Hydrocarbons
- Aliphatic Chain Hydrocarbons
- Aldehydes
- Acyl Chlorides
- Alcohols
- Ureas
- Trifluoromethyls
- Thioureas
- Thiophenols
- Thiols
- Thioesters
- Sulfoxides
- Sulfonyl Hydrazides
- Sulfonic Acids
- Sulfonyl Chlorides
- Sulfonates
- Sulfones
- Sulfides
- Sulfamides
- Phosphoruses
- Oximes
- Phenols
- Nitroes
- Nitrates and Nitrites
- Nitriles
- Ketones
- Isocyanides
- Isocyanates and Isothiocyanates
- Iodides
- Hydroxylamines
- Hydrazones
- Hydrazines
- Hydrazides
- Guanidines
- Fluorinated Building Blocks
- Ethers
- Esters
- Diazoes
- Difluoromethyls
- Chlorides
- Carboxylic Acid Salts
- Carboxylic Acids
- Bromides
- Benzyl Chlorides
- Azoes
- Benzyl bromides
- Organometallic Reagents
- SUPPORT
- RESOURCES
- ABOUT US
- CONTACT US